Deploy Multi-Cloud Applications
This tutorial explains how to deploy multi-cloud applications using resource definitions to abstract away complex configurations.
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure to prepare the necessary resources and complete the following configuration tasks.
Connector Configuration
- Navigate to the
defaultproject >Connectors> ClickNew Connector, choose the connector type asCloud Provider, enter the name "alibaba", select the environment type asProduction, and chooseAlibabaas the type. Enter other required information to complete the configuration. - Click
New Connectoragain, enter the name "aws", select the environment type asProduction, and chooseAWSas the type. Enter other required information to complete the configuration.
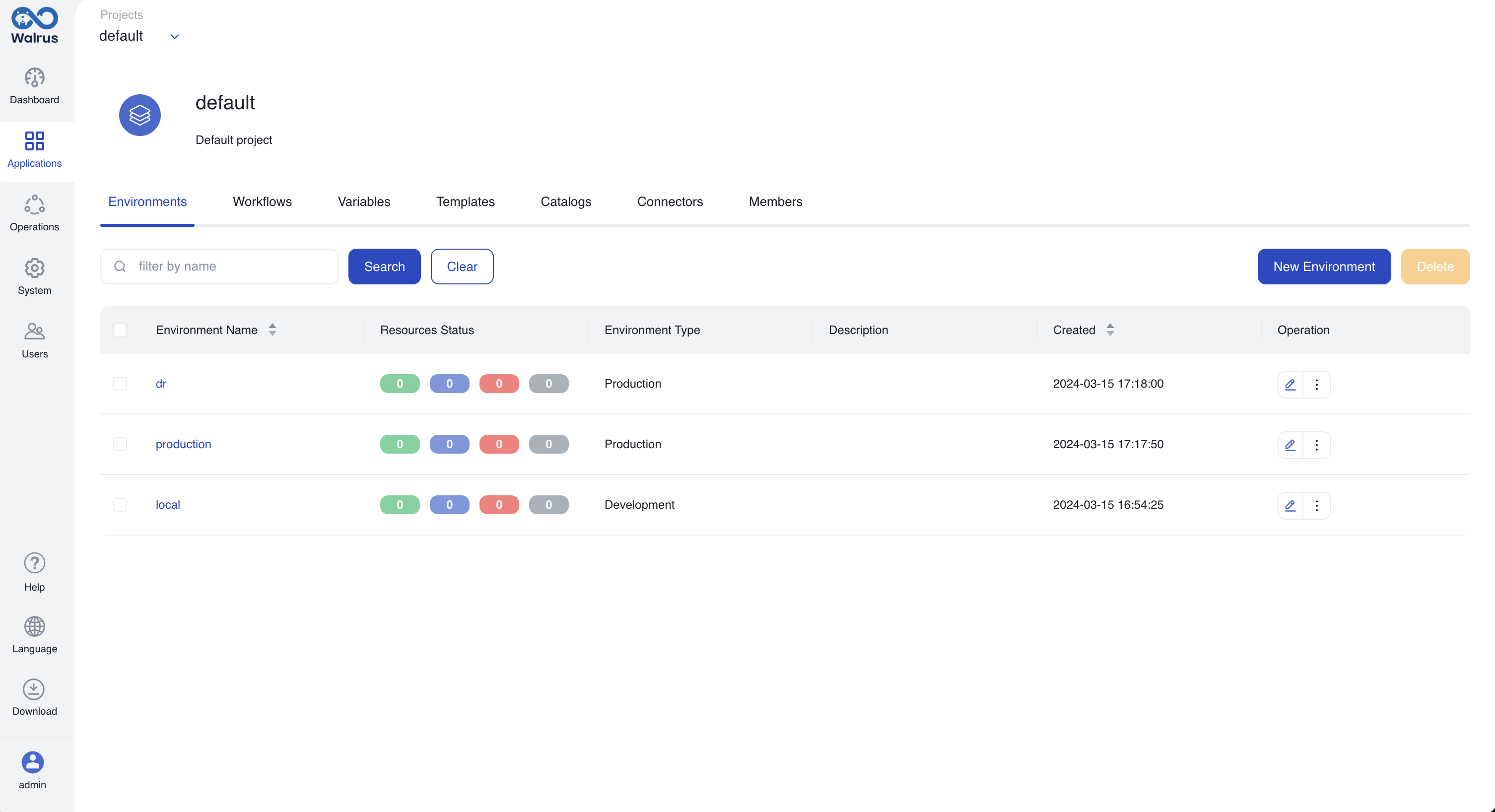
Environment Setup
- Navigate to the
defaultproject >Environments> ClickNew Environment, enter the name "production", associate it with the connector named "alibaba" created earlier for production deployment. - Create another environment named "dr", associate it with the connector named "aws" created earlier for cloud disaster recovery (DR) purposes.
- Include the
localenvironment provided by default in thedefaultproject. Now we have a total of three environments:local,production, anddr.
Download Walrus CLI
- Install Walrus CLI according to the documentation.
Deploy Multi-Cloud Applications
Create Resource Definitions
- Click on
Operationsin the left navigation bar. - Go to the
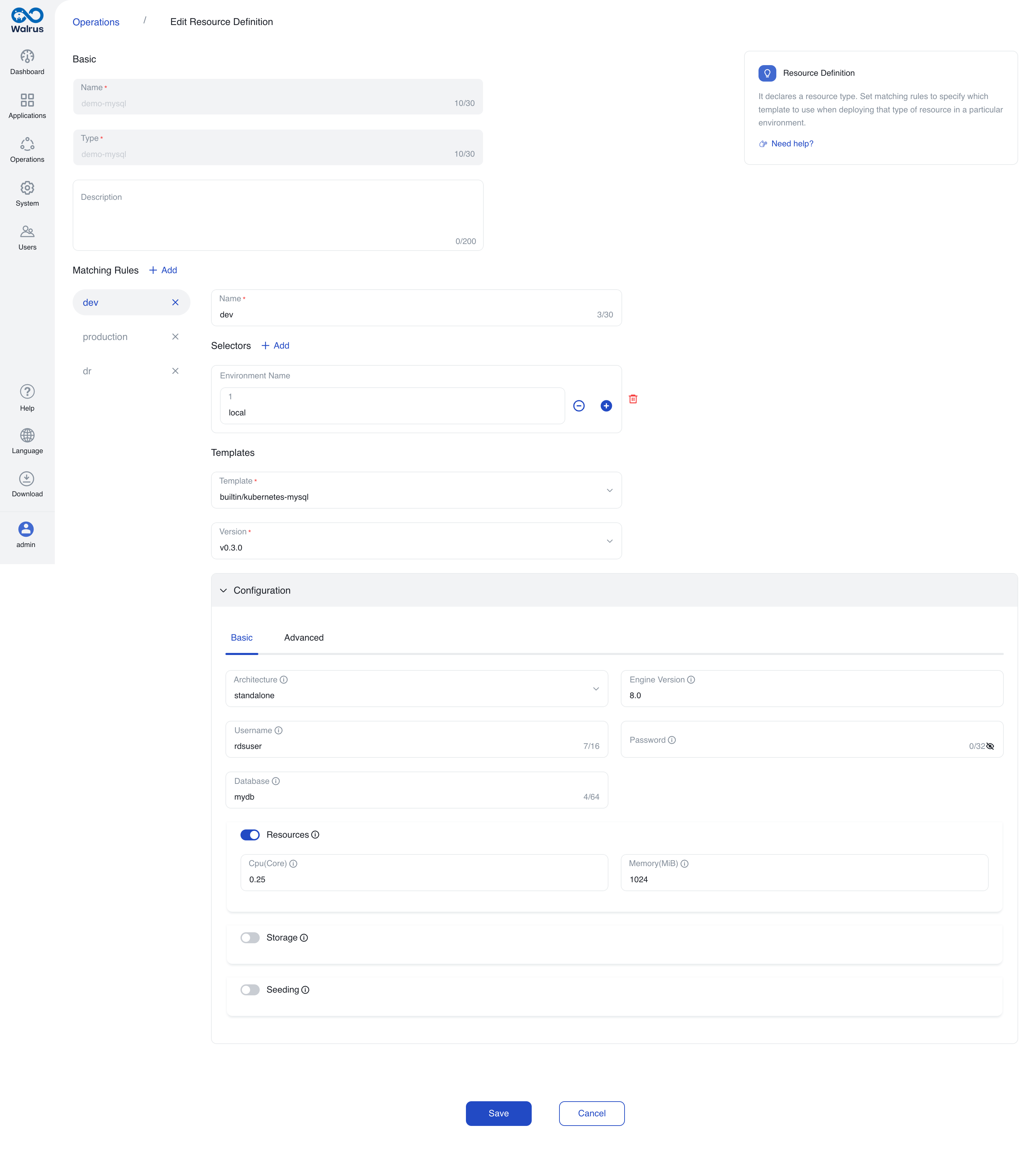
Resource Definitionstab, click onNew Resource Definition, enter the resource definition name "demo-mysql", and select the type "demo-mysql". - Create a matching rule named "dev" to represent the development environment. Add a selector, choose the environment name, and enter "local" as the name. Use the latest version of the template
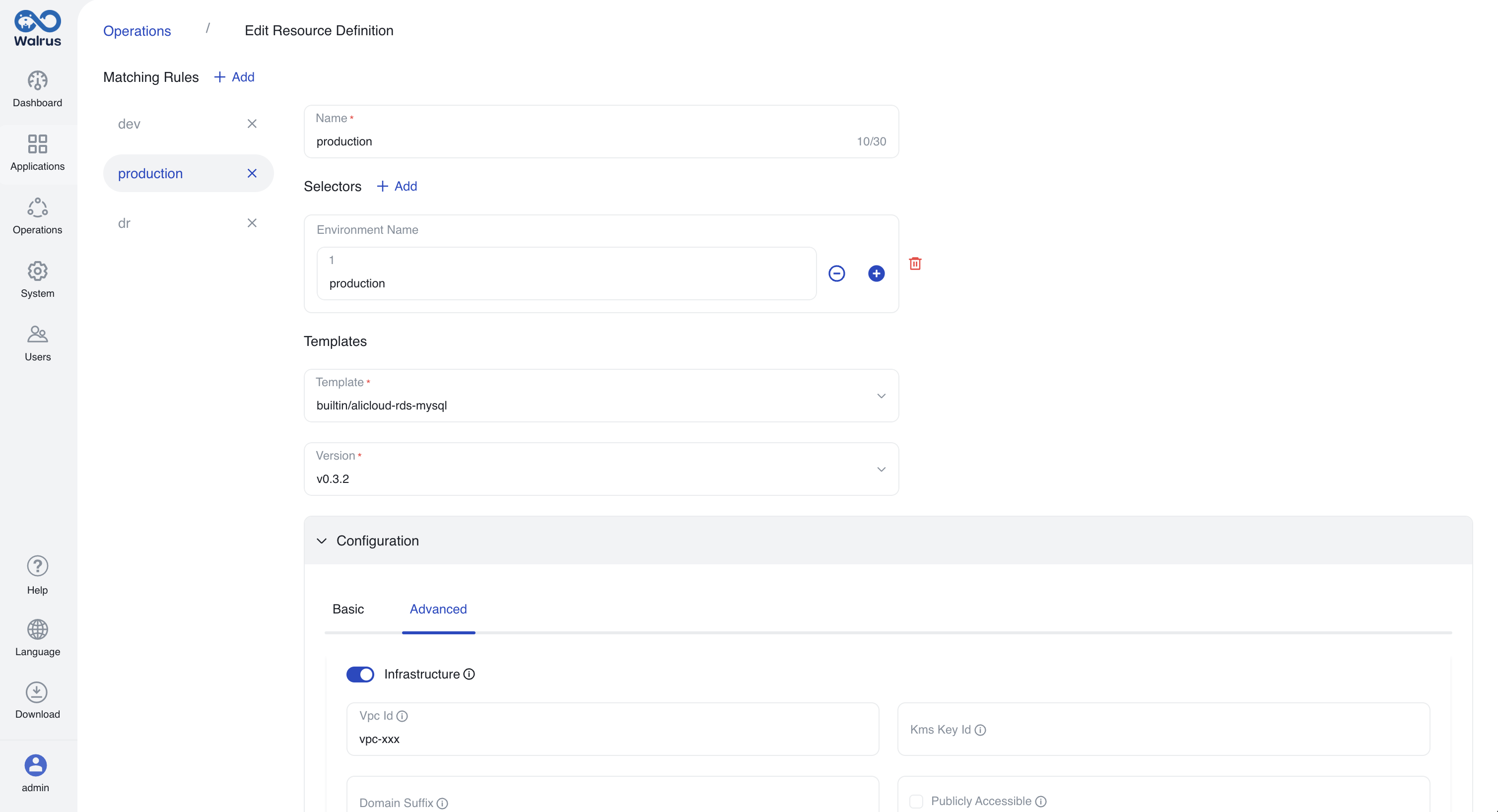
builtin/kubernetes-mysql, and allocate CPU and memory resources in the predefined configuration section. - Create another matching rule named "production" for the production environment. Add a selector, choose the environment name, and enter "production". Use the latest version of the template
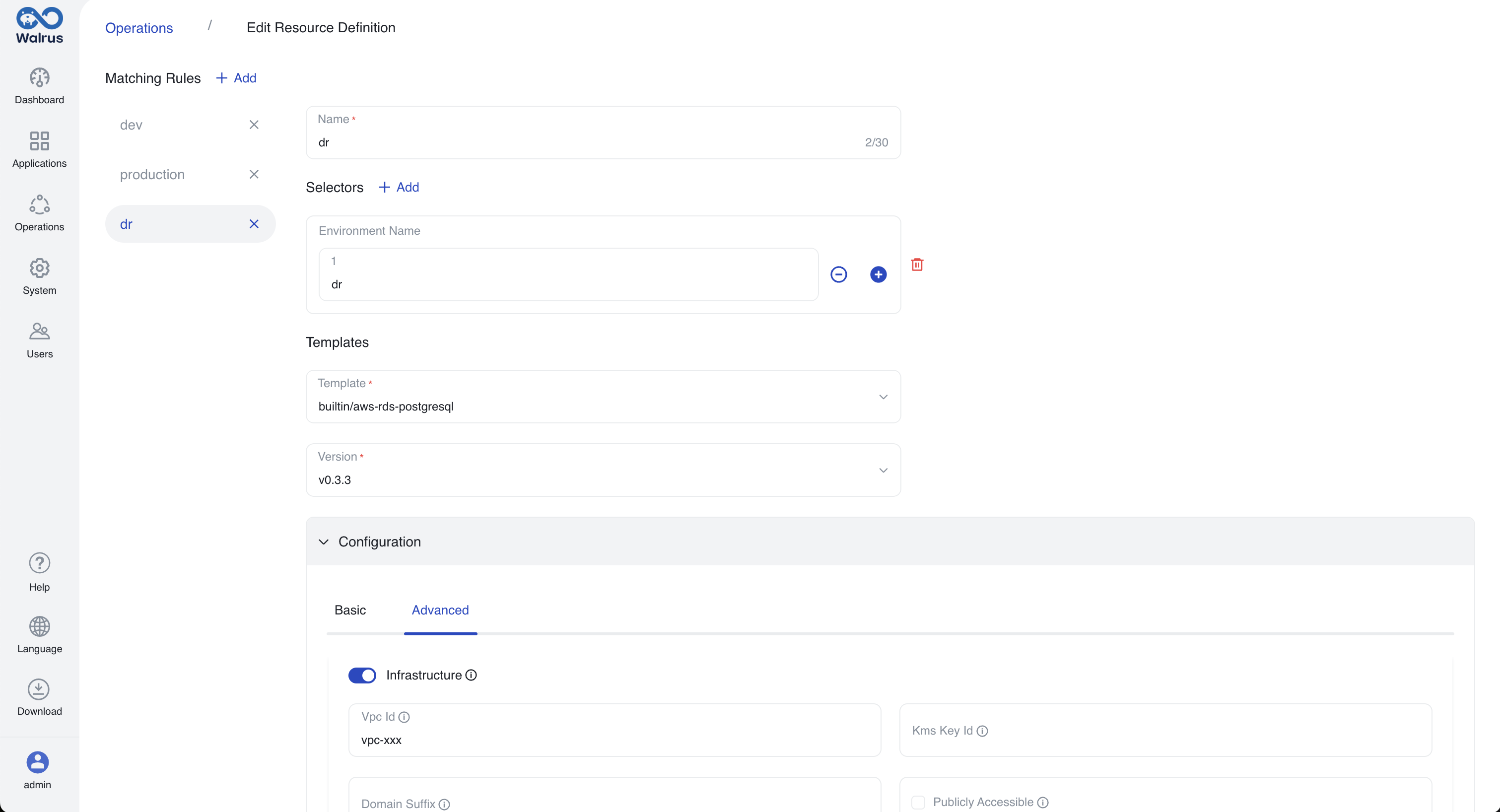
builtin/alicloud-rds-mysqland configure theVpc Idin the predefined configuration section. This eliminates the need for users to input theVpc Idwhen creating resources using this definition. - Create a matching rule named "dr" for the disaster recovery environment. Add a selector, choose the environment name, and enter "dr". Use the latest version of the template
builtin/aws-rds-mysqland configure theVpc Idin the predefined configuration section.
Once configured, the resource definition includes the following matching rules.
Resource definition rule one.
Resource definition rule two.
Resource definition rule three.
- Customize UI styling configurations. After configuring matching rules, Walrus intelligently renders UI styles based on the configuration. Administrators can customize UI styles as needed.
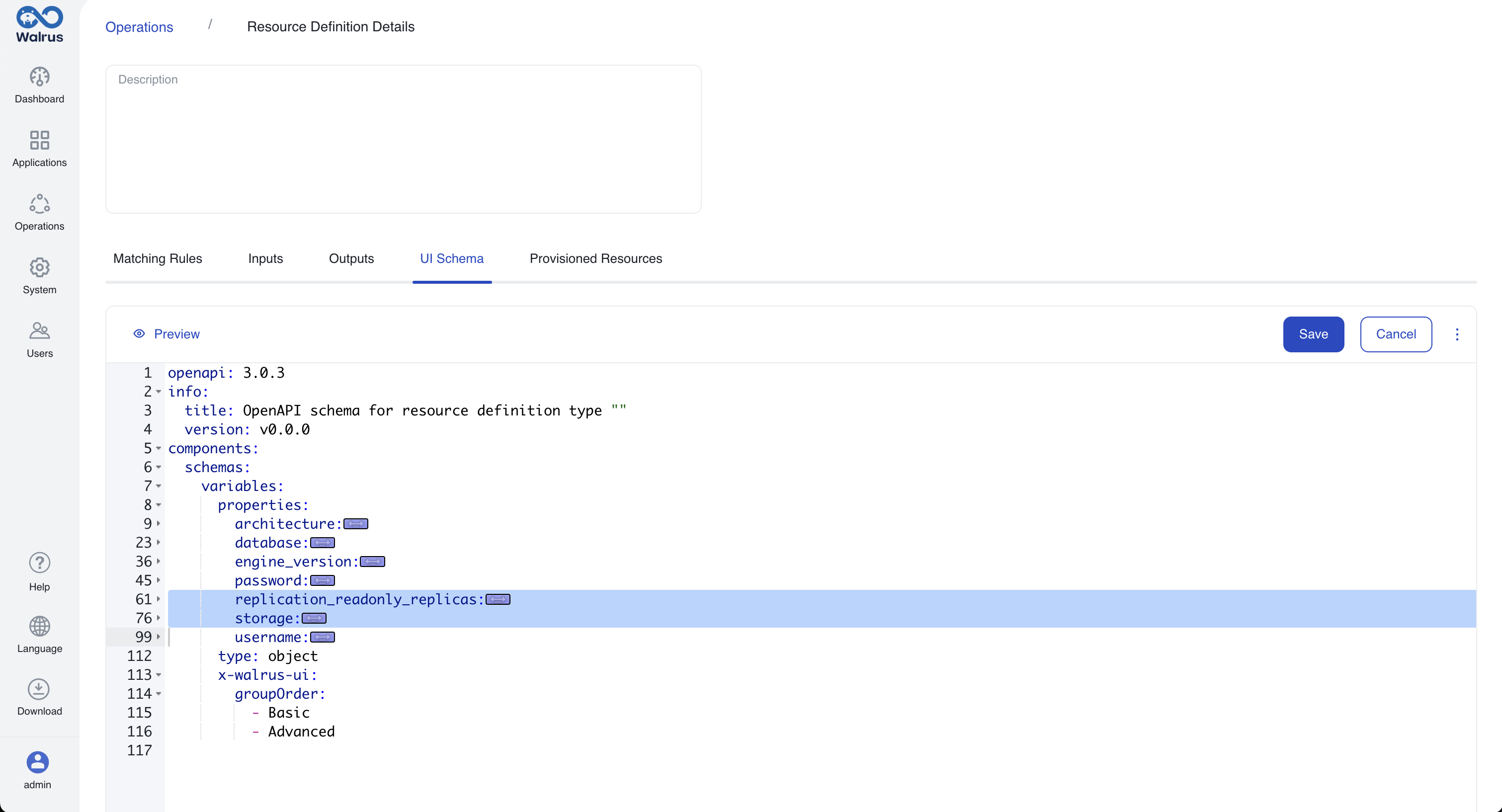
- Go to the resource definition "demo-mysql" >
UI Schematab, clickPreviewto see the automatically generated UI style. ClickEdit, here we remove some complex configurations (replication_readonly_replicas,storage) and leave common configurations to support quick deployment.
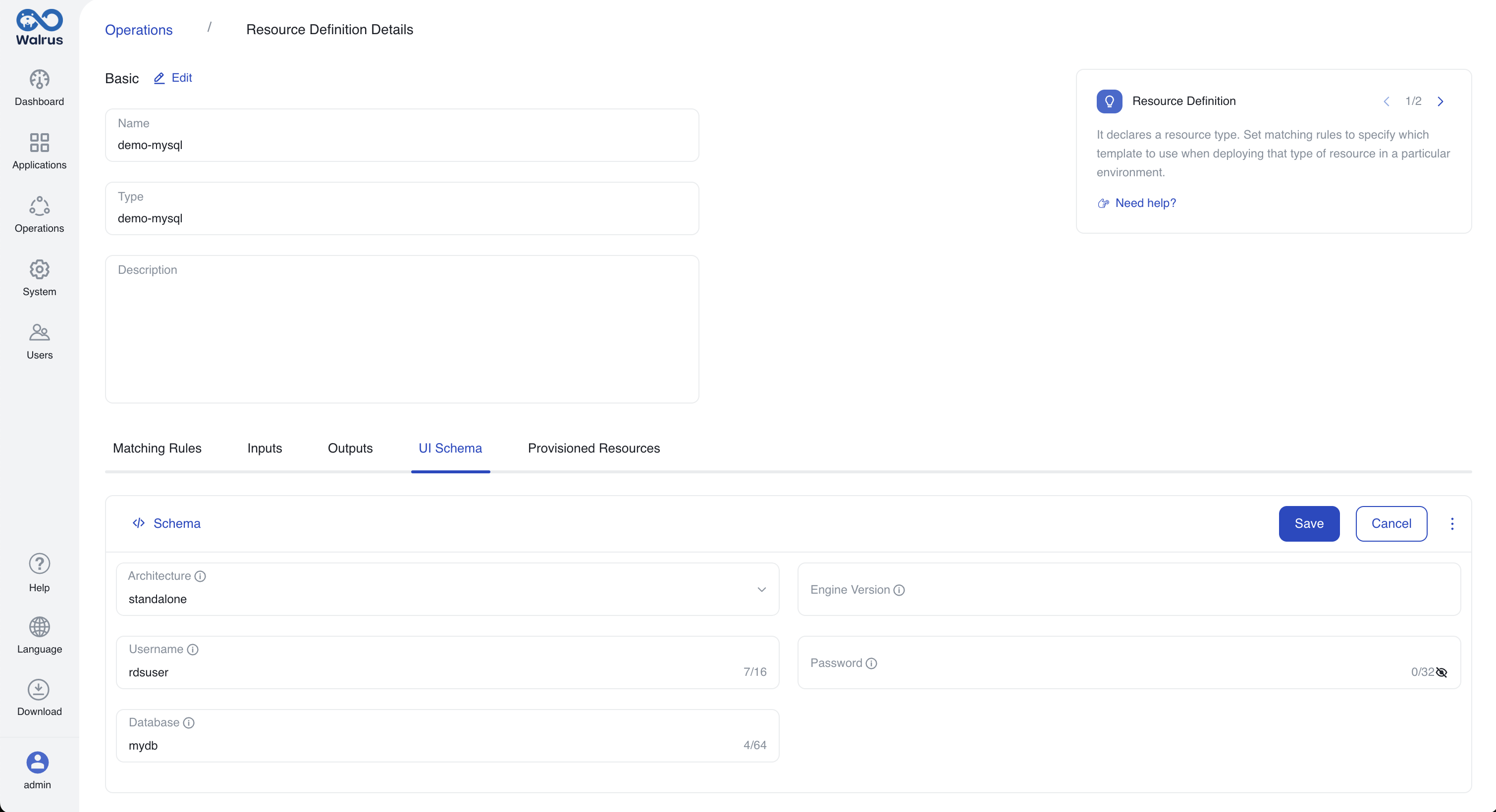
- Below are the completed UI styles after configuration.
Deploy Multi-Cloud Applications
With the configured resource definitions, we can now create multi-cloud applications.
- Go to
Applications>localenvironment > ClickNew Resource. - Enter the resource name, choose the resource type "demo-mysql" that we just created, input architecture, database version, and other configurations, then click
Saveto deploy. - Go to the
productionenvironment > ClickNew Resource, select the resource type "demo-mysql" again, input configurations, and complete the deployment. - Go to the
drenvironment > ClickNew Resource, select the resource type "demo-mysql" again, input configurations, and complete the deployment. - All three environments have created resources of type "demo-mysql". The
localenvironment is connected to a Kubernetes connector, theproductionenvironment is connected to an Alibaba connector, and thedrenvironment is connected to an AWS connector. You can see that different environments dynamically create corresponding resources based on the current environment.
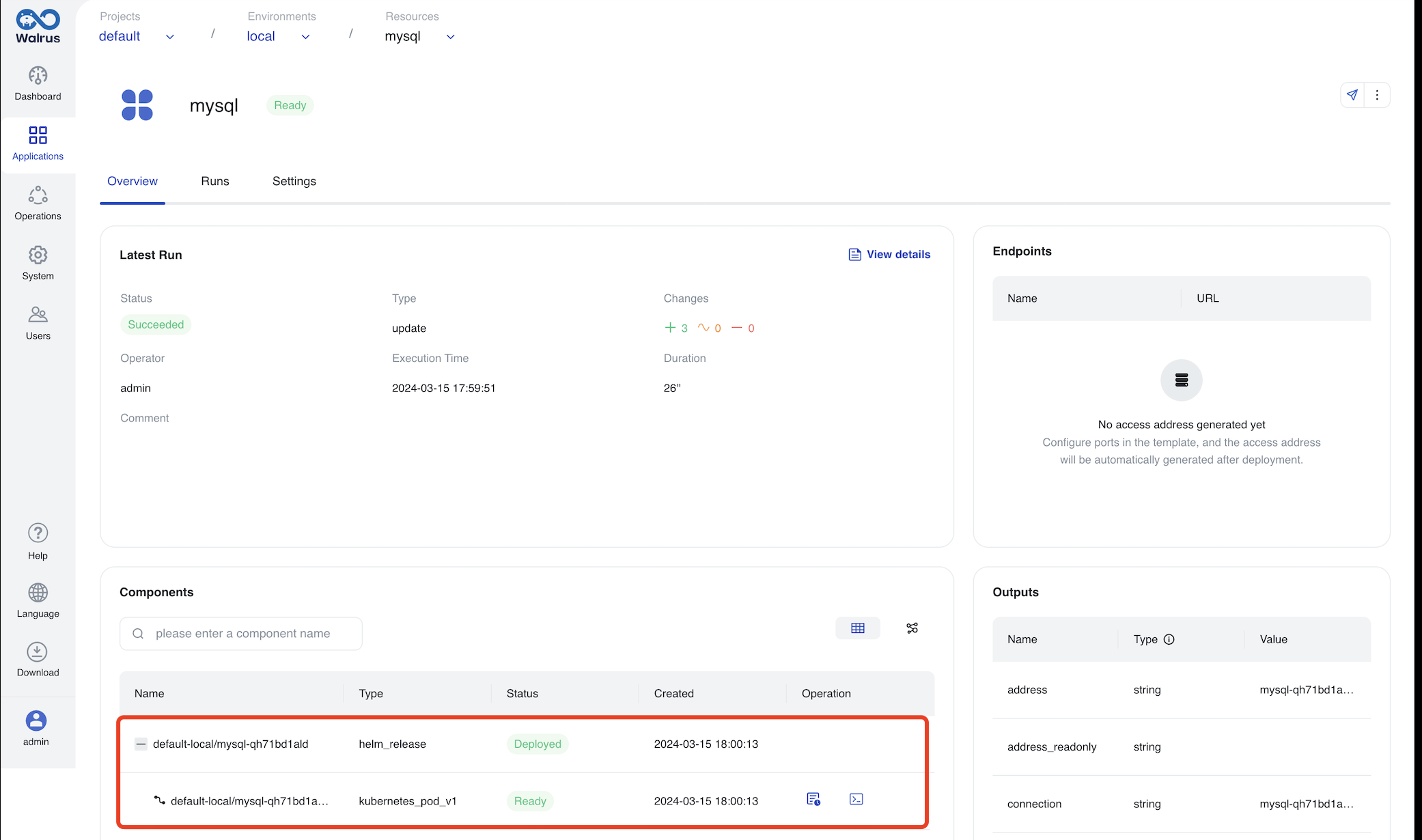
The local environment creates a MySQL container in the Kubernetes cluster.
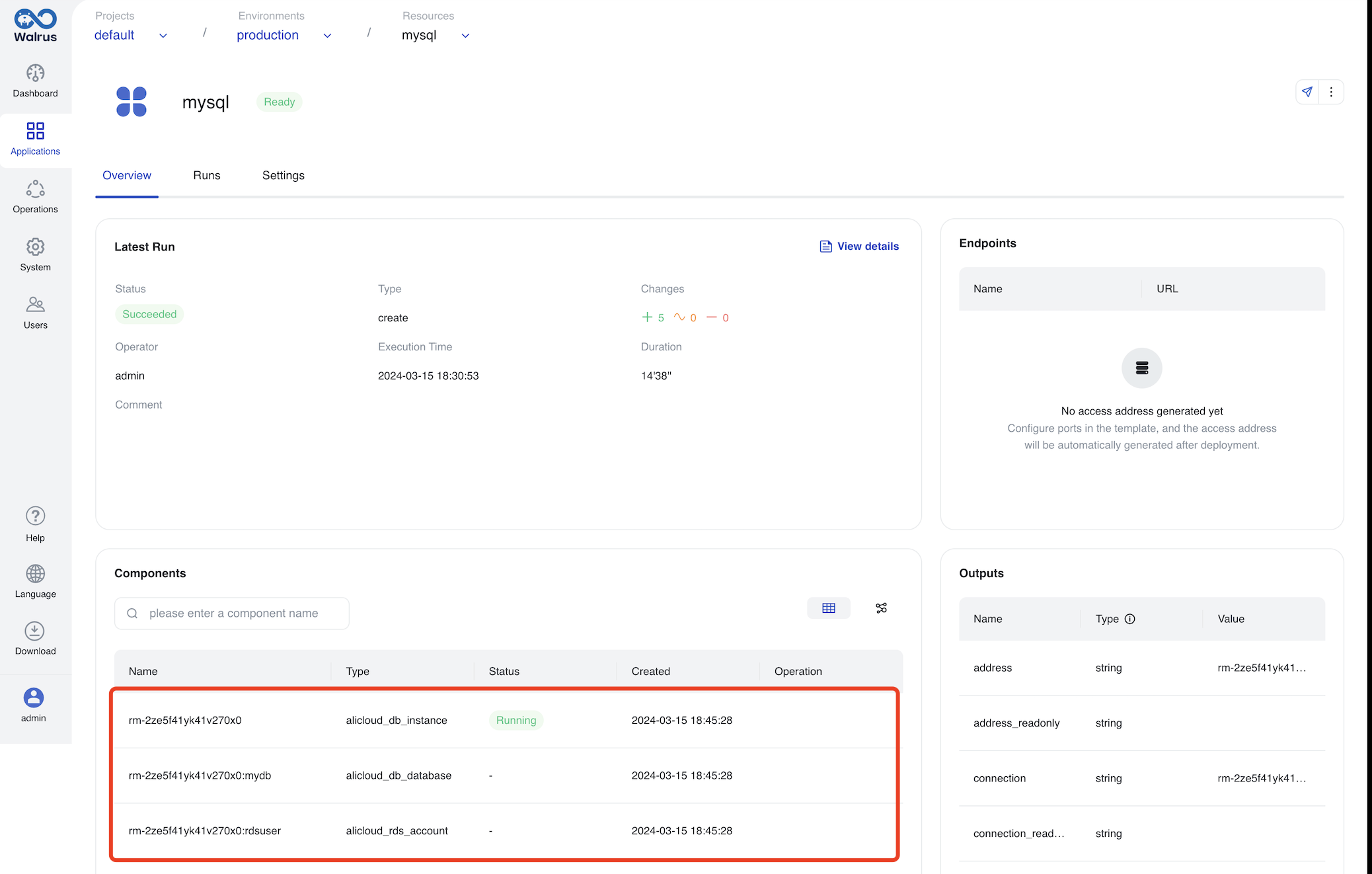
The production environment creates an RDS service in Alibaba Cloud.
The dr environment creates the corresponding RDS service in AWS Cloud.
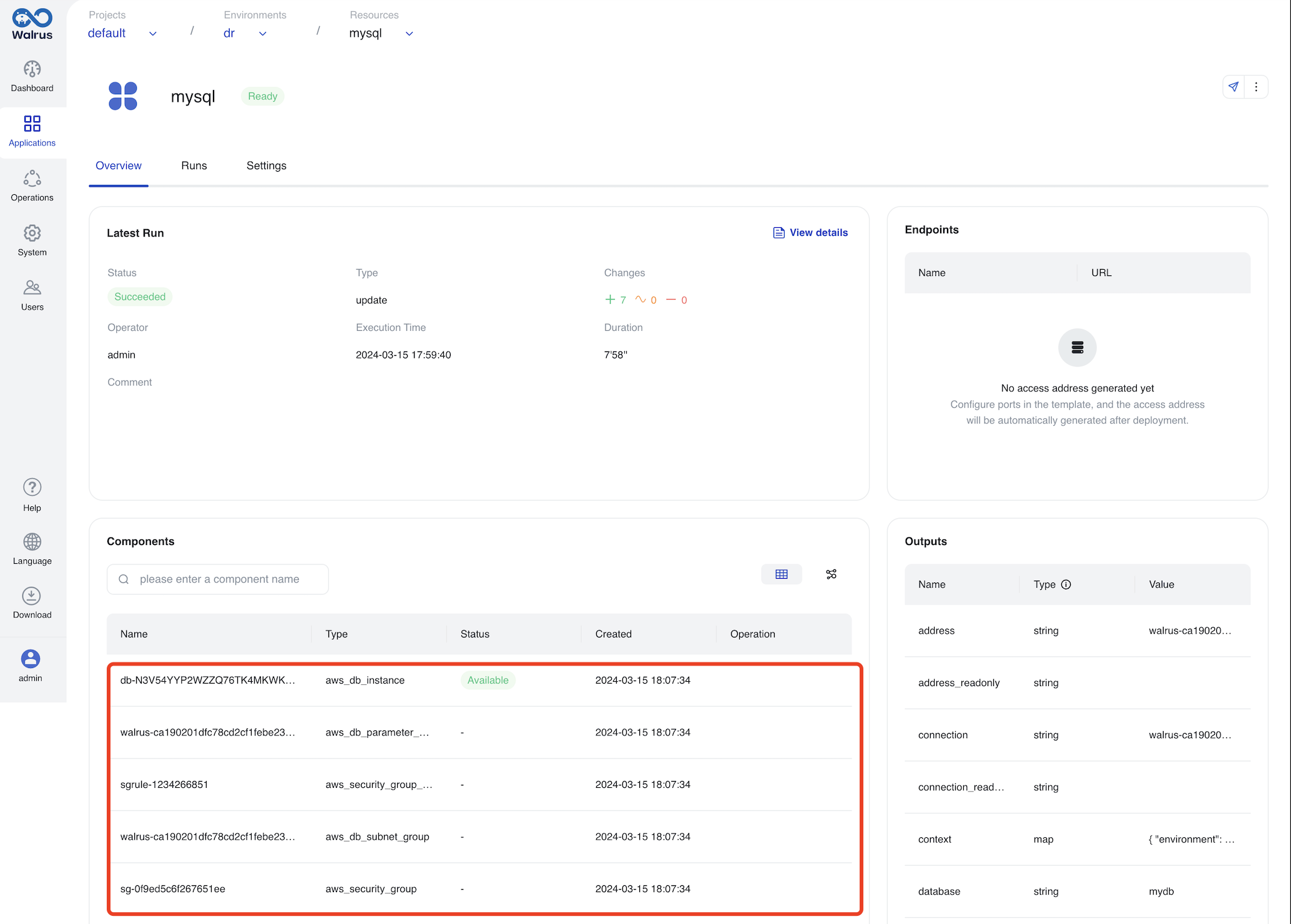
Deploy Multi-Cloud Applications via Walrus File
In addition to deploy multi-cloud applications via UI, you can achieve the same effect using a Walrus file.
- Prepare the app.yaml with the following content:
version: v1
resources:
- name: mysql
type: mysql
attributes:
architecture: standalone
database: mydb
engine_version: "8.0"
username: rdsuser
- Run the command to deploy to different environments.
# Deploy to the local environment
walrus apply -f app.yaml -p default -e local
# Deploy to the production environment
walrus apply -f app.yaml -p default -e production
# Deploy to the dr environment
walrus apply -f app.yaml -p default -e dr
Deploying via CLI allows you to reuse the same Walrus file to deploy multi-cloud applications to different environments.
With this, we have completed configuring resource definitions to simplify application deployment and deploying multi-cloud applications.